
Honoring Walter Szrek: Recipient of the NASPL Powers Award September 2, 2025
Reflecting on those early days, Don Stanford, founding member and former long-term CTO of GTECH Corporation shared:
“ Walter Szrek was […]

pop test
Interested in future-proof, turnkey RNG security technologies?
Szrek2Solutions provides complete secure solutions for RNG platforms and electronic draw systems for all lottery games.
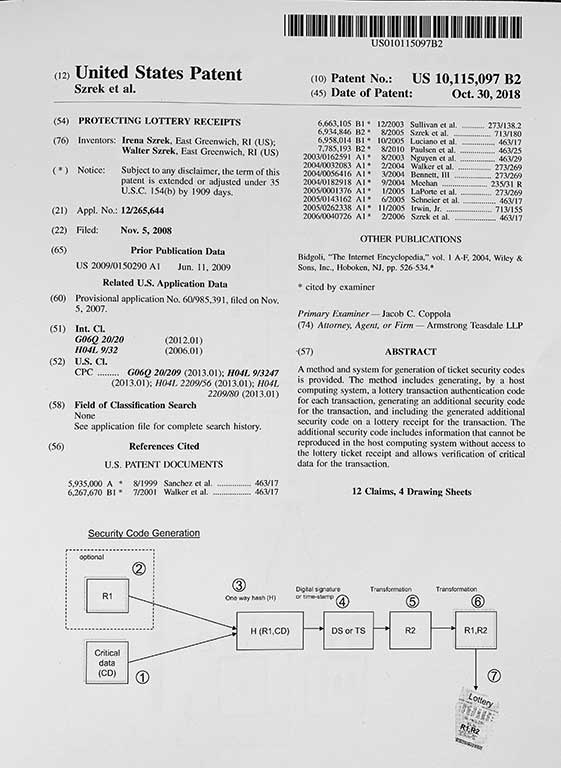
When the digital signature is used as random number seed, every specific random number derived from this seed is also verifiable. Because an incorruptible clock is also digitally signed, the time of the signing operation is also verifiable. Each time the HSM generates a signature, the internal embedded counter is incremented and signed. This way each signature and every random number generated is accounted for. In addition, the method allows verification of the specific HSM being used and any additional draw information: since draw information is digitally signed (e.g. personnel conducting the draw, etc.) it can be verified. LYNKS II Security certified by NIST.
Szrek provides a secure and reliable method for random numbers generation based on its patented method of RNG non-repudiation (patent nr 6,934,846). The method is based on asymmetric properties of digital signatures, where a digital signature generated with a private key is used as a random number seed. Random numbers are derived from the seed, and since the seed is a digital signature of draw data it can be verified using the public key, along with the random numbers and the draw data. For digital
signing, Trusted Draw uses secure and tamper evident NIST certified Hardware Security Modules (HSMs).
The unique benefit of Szrek RNG technology is that generated unpredictable and unbiased random numbers can be mathematically verified to detect any potential fraud. The RNG has been certified by several US and international independent labs and has been used successfully since 2005 by numerous lottery operators and state licensed lotteries around the world.
Does certification ensure RNG security?
What kind of security measures are there to protect an RNG?
What are the limitations of preventive security?
What type of audit is available for RNG systems?

Draw time substitution after the results are generated
The time stamp for offline draws can be altered, meaning draw results can be known before they are published.
Hardware substitution for alternative hardware that produces predictable results
Such substitution may go unnoticed unless there is a way to identify the hardware used for each draw
Substitution of numbers drawn after the results are generated
An insider can substitute the winning numbers and this can go unnoticed if the RNG system does not provide verification methods and the results are not consistently verified.
Software substitution during initial delivery, during maintenance, or later
Certification, pre-post testing, verification of program checksums, system scans, verification tests, and post-mortem testing may not find the hidden code.
Phishing or attempting multiple RNG generations to obtain desired outcomes
Traditional RNGs allow for multiple generations and it may be impossible to know how many have occurred.
Hardware deterioration results in hardware not performing RNG functions safely or properly
Traditional RNGs may not have specific hardware verification tests in place.
Inadequate RNG design & implementation detection of software and hardware errors and malfunctions
Software designed to check for errors, detect hardware issues and malfunction



